Weathering-and-Dispersant-Learn-More
Learn More - Weathering and dispersant testing
Learn More -
Weathering and dispersant testing
IPL’s weathering and dispersant testing of crude oil plays an important role in minimising risks associated with potential oil spills.
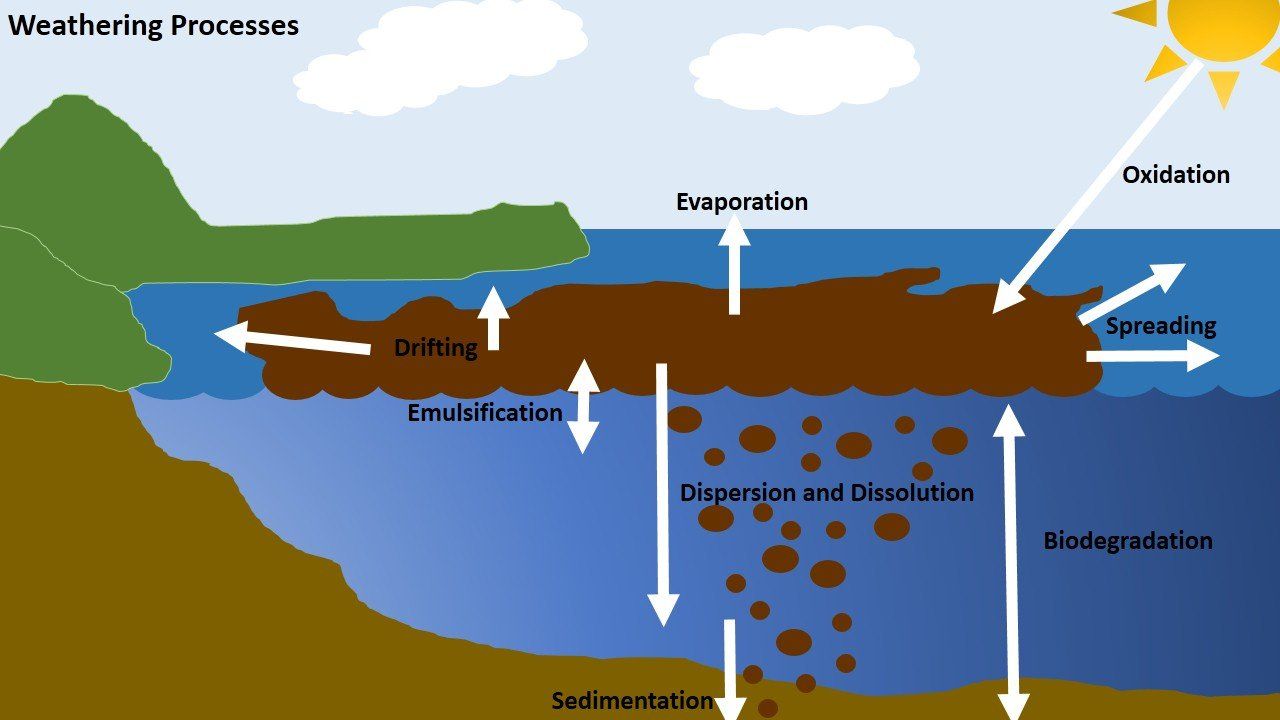
What is Weathering?
There are several weathering processes which affect how an oil weathers in the event of an open ocean spill. Each of these processes is largely dependent on sea state and prevailing weather conditions at the time of a spill, but all have the ability to affect the chemical and physical properties of the oil. Weathering testing is prediction testing of oil properties under controlled weathered conditions. It is required in the New Zealand discharge management planning process because this information enables the oil explorer to plan what actions to take in the event of an open ocean spill.
Maritime NZ is the agency responsible for ensuring operators and producers of all New Zealand offshore installations, have a plan in place to manage their emergency response and any discharge activities. The Marine Protection Rules Part 200 includes the rules and regulations under which the petroleum explorers and producers have to operate.
A Discharge Management Plan (DMP) is valid for 3 years. DMPs have to be carried out 2 months before the operations begin or 2 months before expiry for DMP renewals. Any modification to DMPs during the 3 year timeframe needs to be notified. Act 200.4 contains all the requirements of a DMP. As part of the Discharge Management Plan, a thorough risk identification, prevention and assessment needs to be carried out. Matters such as location details, installation arrangements, operations taking place at the installation, oils stored, description of processes, details of the activities representing a risk of pollution originating from an oil spill and identification of potential environmental impacts have to be addressed.
By bringing this key technology to NZ, IPL plays an important role in the DMP process by providing the required information about the oils produced by the installation. Our testing capabilities enables us to provide the oils’ physical properties, weathering information and effectiveness of dispersants. Below are the list of tests required in a DMP.
What is Dispersant Testing?
Oil spill dispersants can be used after an oil spill has occurred to break up the spilt oil into tiny micelles. These micelles are then able to suspend into the water column where they are biodegraded by microorganisms.
Use of oil spill dispersants is included in the discharge management planning process. Testing ensures oil explorers know which oil spill dispersants may be effective and how long they remain effective for.
Prediction testing allows the oil explorer to be prepared and act quickly in the event of an emergency, reducing the effects the oil spill will have on the surrounding environment.
| Oil physical properties | Weathering | Dispersant Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Pour point | Evaporation rates | Dispersant effectiveness on fresh and weathered oil for 12, 24 and 48 horus |
| Visocsity | Emulsion forming tendencies | |
| Density | Changes in oil properties at 12, 24 and 48 hours | |
| API gravity | ||
| Wax content | ||
| Asphaltene |
Go back to weathering and dispersant testing
In New Zealand, weathering and dispersant testing is required as part of the Discharge Management Plan for all offshore oil exploration.
other related services

Oil and Gas Testing Services

Crude Assay for O&G Explorers

Crude Assay for O&G Producers
Dedicated to providing quality lab testing services
About IPL
Established in July 1999, Independent Petroleum Laboratory Limited (IPL) is a fully independent laboratory that provides specialist Fuels, Biofuels, Industrial and Environmental laboratory testing services to a wide range of customers throughout New Zealand and the South West Pacific.
Get the latest information and promotions in your inbox
Newsletter
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Oops, there was an error sending your message.
Please try again later.
Please try again later.
© 2024
IPL : Website Design Auckland by Fuel Design Ltd